Biophilia: Nature & Design
/You may have seen the terms "biophilia" or "biophilic design" brandished around the internet lately, posted between beautiful images of sprawling home design and architecture filled with plants and nature-inspired sculpture installations. Biophilia isn't new–but it is a growing discipline in home design. If you are interested in healthy living or are a building owner, it's a subject worth learning.
Biophilia is our innate desire to be close to nature–and biophilic design aims to make healthy and comfortable interiors by meaningfully incorporating natural elements into our home and work environments. Los Angeles-based interior designer Sarah Barnard sat down with me to explain how she uses biophilic principles to create healthful, smart spaces for her clients. "It's intuitive when you think about it. Biophilia exists because we are comforted by nature, and we all understand that on some level. Nobody wants to live in a little grey box–we want to live in open spaces connected with the environment, plant-life, and the seasons."
Biophilic design puts a few simple principles to use to create spaces that are both visually beautiful and spiritually healthful. As more and more of us make our careers our focus, calmness, serenity and healthy living can be challenging to achieve without the help of nature and smart design. There are years of study to support what we already know in our bones: spaces that have nature incorporated are more appealing to us, and they have marked health benefits.
Terrapin Bright Green is a consulting firm specializing in sustainability to create a healthy, prosperous, and regenerative future for all. They produce workshops, research, planning, guidelines, and product development. They have researched biophilia and organized their findings into 14 principles of biophilic design and have studied the effects of biophilia on our health and wellness. For the most part, many of the principles are simple and intuitive, such as ‘Visual Connection with Nature,’ which is just what it sounds like: adding natural elements or a view to nature into your space.However if you’d like to read an in-depth, thorough explanation of all 14 principles, you can see the results of Terrapin’s research here: https://www.terrapinbrightgreen.com/reports/14-patterns/ . For today, we need only to talk about the three subcategories of the design principles: Nature in the Space, Natural Analogies, and Nature of the Space.
Nature in the space refers to the presence of natural elements in an interior. For example, that could mean having plants, shells, or water features. But it could also mean more abstract features, like natural light or light that changes throughout the day, air circulation, and a view to the outdoors. “What you exclude is just as important as what you include,” said Barnard. “I choose art made with natural materials or vintage art that has off-gassed to avoid putting noxious smells or chemicals into a space. Indoor air quality accounts for part of how we feel about our homes and how comfortable we are.” All of her designs include live plants, working in tandem with HEPA filtration systems to contribute improved air quality, a non-visual connection with nature.
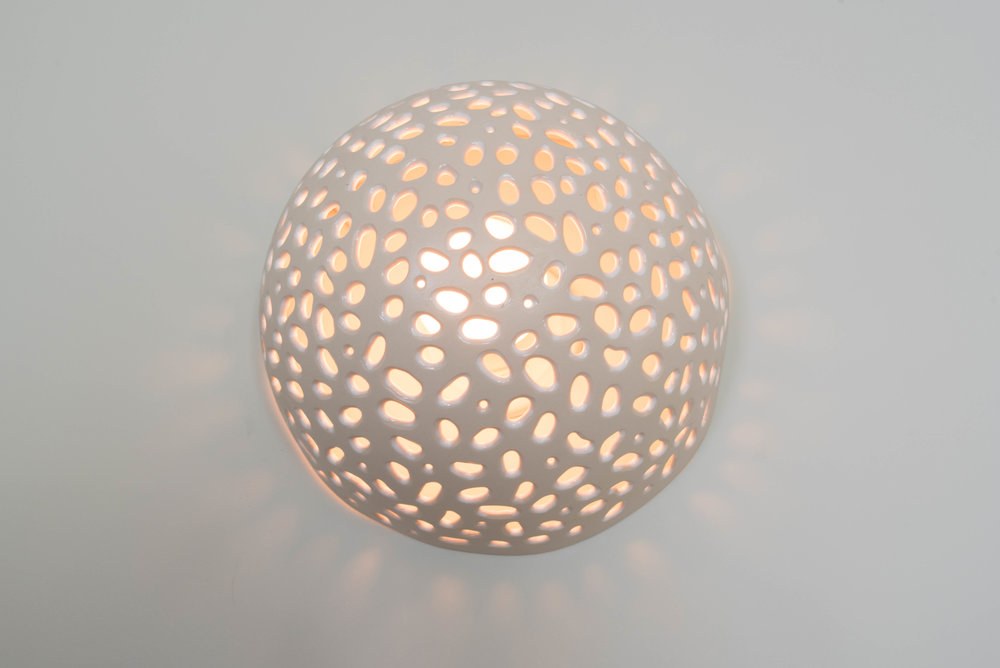
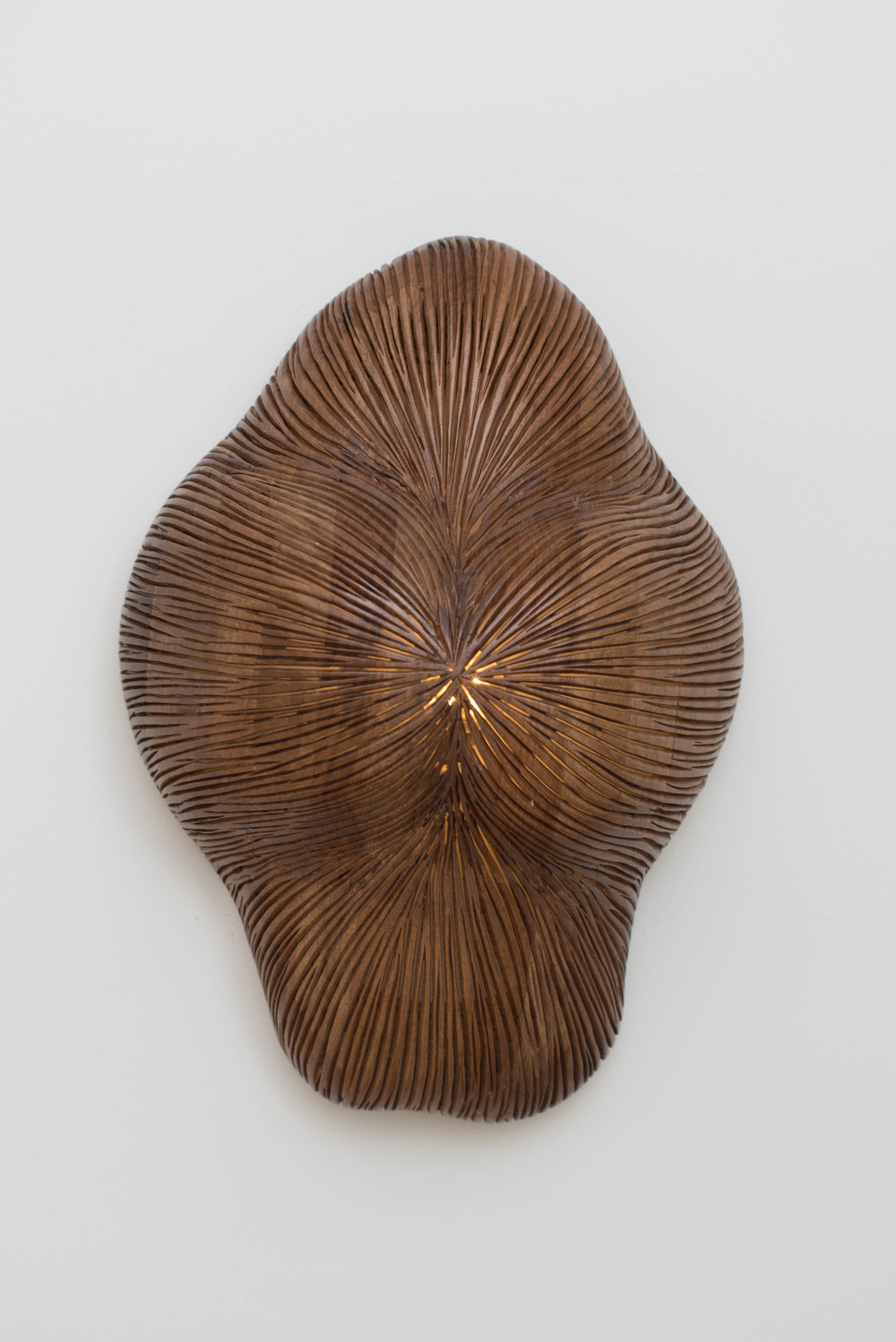
Natural analogies refers to art and forms inspired by nature: a light fixture that looks like a plant or a sculpture that looks like an animal, for example. A good designer will find natural forms and art for you to choose from so you can have art that imitates nature. Barnard walked me through a project she made custom light fixtures for. “The home was beside the ocean, and I wanted to make something inspired by the beautiful surroundings of that space. I started by sketching forms inspired by coral reefs, and I made miniatures in clay by hand. When they were ready, I had them fabricated by a local craftsman. Having forms that imitated the shape and texture of coral and having light cast in beautiful organic patterns made the space feel natural and serene.”
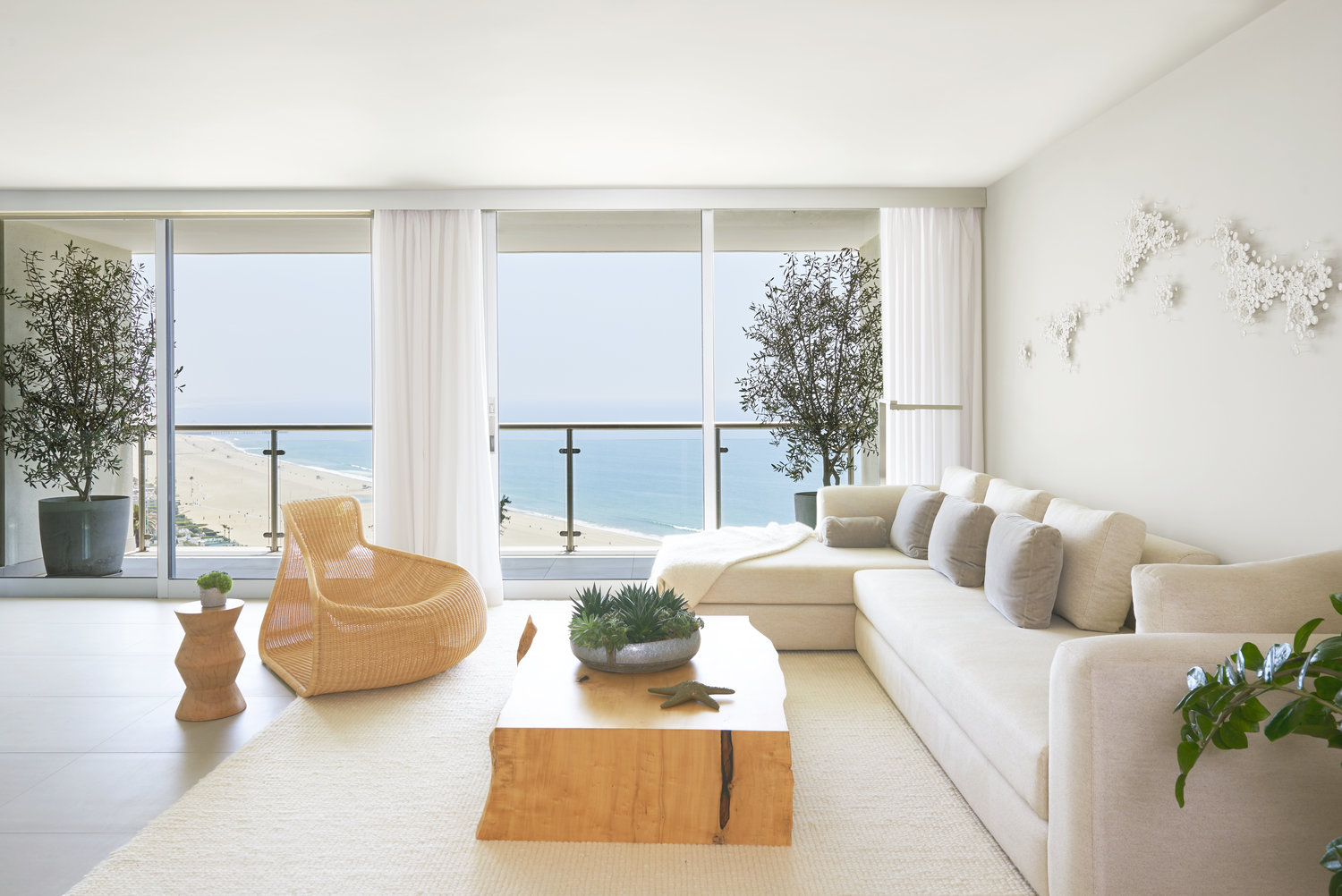
Nature of the space means making the space itself seem like nature. Having a large open space through which you can see an expanse of space, as well as an enclosed room that feels safe fulfills this need. When asked for an example of how Nature of the Space might be used, Barnard said “I finished a project recently where the space had floor-to-ceiling windows with a view to the ocean. I selected low profile furniture to preserve the open space of the room and the sightline to the sea.”
Terrapin also explains that there are three basic types of “nature-health” relationships: cognitive functionality and performance, psychological health and well-being, and physiological health and well-being. Cognitive functionality and performance is our mental acuity and focus. Psychological health and well-being refers to our mood, perception, and emotional state. Physiological health and well-being is our bodily health and performance.
All three areas of well-being see improvement when the 14 principles of biophilic design are applied in a space. The benefits have been thoroughly studied: each principle has been individually tested and shown improvements such as concentration, stress hormone levels, overall happiness, and numerous other positive effects.
In fact, research by other sources has yielded similar results. The Human Spaces Global Report also found greater levels of well being in subjects with a view of natural elements rather than urban settings, according to a recent article by Steelcase’s magazine 360.
Steelcase, the largest furniture manufacturer in the world, is dedicated to sustainability, innovation, and wellness. They too have invested into researching biophilia in order to produce furniture for healthy, sustainable spaces. They describe the human experience with nature in four categories:
Sensory richness: mixing colors, textures, sizes and shapes. Varied elements in a space mimics nature and puts us at ease.
Natural rhythms and signals: anything that reminds us of natural processes can help restore us. Natural lighting that allows real sunlight, or artificial light that changes to mimic natural light.
Challenges in nature: the idea is that our challenging environment is what pushed humanity to grow into what we are today, so there should be encouragement towards effort.
Local distinctiveness: having a feature that does not repeat anywhere else in the building can help large offices from becoming soulless or bleak. Reserving a certain material or color for one room can make it and the surrounding space more special and pleasant.
These four principles are a useful way to understand how we are affected by nature, and offer another way to begin tackling the design challenges you may be facing in your home or workspace. Whether you use these four facets or the 14 principles of biophilic design as a jumping off point to improve your space, a deeper connection with nature is healthy and beneficial.
“When you strip it down to basics, using biophilic design means including pieces of nature in the design, elements inspired by nature, and mimicking natural environments with layout, architecture and planning,” Barnard said. Homeowners and building owners especially might consider taking these premises into account in order to make their home or office a place that promotes their mental and physical wellbeing. Getting started can be as simple as purchasing a few plants. If you aren’t sure where to go from there, a designer can help you put all the principles into practice. Ideally, your space incorporates nature, smart design and healthy living.
Photos by Chas Metivier and Steven DeWall
Sarah Barnard designs healthy, happy, personalized spaces that are deeply connected to nature and art.
To learn more about Sarah Barnard Design, please visit www.SarahBarnard.com.